We are Launching Live Zoom Classes for 9th and 10th-grade Students. The first batch is from 7th April 2025. Register for a Free demo class.
Class 8 Science NCERT Notes – Chapter 3: Health, The Ultimate Treasure (PDF, MindMap, Q&A, Quizzes)
Here are detailed study notes from Chapter 3, “Health: The Ultimate Treasure,” from the NCERT Class 8 Science book. At the end, some relevant questions and answers are provided to help students prepare effectively for exams and class activities.
What is Health?
- Health means more than just not falling sick; it includes complete physical, mental, and social well-being.
- A healthy person feels good physically, stays positive, and has strong relationships.
- The WHO defines health as “a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, and not merely the absence of disease.”
Aspects of Health
- Health has three main aspects:
- Physical health: Proper body function, no illness, energy for daily work.
- Mental health: Positive attitude, stress handling, emotional stability.
- Social health: Good relationships, social interactions, no loneliness.
Ways to Stay Healthy
- Eat balanced and nutritious food.
- Practice personal hygiene (bathing, washing hands).
- Exercise and stay physically active (sports, walking).
- Get adequate sleep and rest.
- Avoid habit-forming substances like tobacco and alcohol.
- Manage stress through yoga, meditation, and socializing with family and friends.
- Limit screen time and spend time in nature.
- Keep the environment clean to avoid diseases caused by pollution or poor sanitation.
Types of Diseases
Communicable Diseases
- Communicable diseases are caused by pathogens like bacteria, viruses, fungi, or worms and spread from person to person.
- Methods of transmission:
- By air (sneezing, coughing)
- By direct or indirect contact
- By contaminated food or water
- By insects (vectors like mosquitoes)
Examples (from Table 3.1)
| Disease | Causal Agent | Key Symptoms | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Common cold | Virus | Sore throat, fever, cough, body ache | Handwashing, covering mouth/nose |
| Chickenpox | Virus | Fever, rashes, blisters | Patient isolation, vaccination |
| Measles | Virus | Fever, rashes | Isolation, hygiene, vaccination |
| Tuberculosis | Bacteria | Cough, fever, fatigue | Avoid close contact, vaccination |
| Hepatitis A | Virus | Jaundice, fever, nausea | Drink boiled water, vaccination |
| Cholera | Bacteria | Diarrhoea, dehydration | Safe water, hygiene, vaccination |
| Typhoid | Bacteria | Fever, headache, diarrhoea | Safe water, hygiene, vaccination |
| Malaria | Protozoa | High fever, chills, sweating | Mosquito nets, repellents, hygiene |
| Dengue | Virus | Fever, headache, joint pain | Mosquito control |
Non-Communicable Diseases
- Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) do not spread between people and are not caused by pathogens.
- Caused by improper lifestyle, genetics, environment, or deficiency of nutrients.
- Examples: Diabetes, heart disease, obesity, cancer, asthma.
Examples (from Table 3.2)
| Disease | Symptoms | Prevention/Lifestyle Change |
|---|---|---|
| Obesity | Excess fat, low activity, breathing trouble | Exercise, healthy eating |
| Diabetes | Frequent urination, tiredness, weight loss | Balanced diet, regular exercise |
| High BP | Headaches, dizziness, fatigue | Stress management, less salt, exercise |
| Anaemia | Weakness, pale skin, fatigue | Iron-rich diet |
How to Prevent Diseases
- Cleanliness: Maintain good personal hygiene and keep surroundings clean.
- Vaccination: Prevents deadly communicable diseases (e.g., polio, measles, hepatitis).
- Safe water and food: Avoids diseases like cholera and typhoid.
- Mosquito control: Prevents malaria, dengue (nets, repellents, removing stagnant water).
- Proper use of antibiotics: Only take antibiotics as prescribed to avoid antibiotic-resistance.
Immunity and Vaccination
- Immunity: The body’s ability to fight diseases. Some people are naturally immune; others develop immunity after vaccination or recovering from an illness.
- Vaccines: Prepare the body by exposing the immune system to a harmless form of the germ, building future protection.
- Antibiotic resistance: Overuse/misuse of antibiotics can lead to resistant bacteria, making infections harder to treat.
Indian Contributions to Health Science
- Ancient systems like Ayurveda advocate a balance of body and mind through food, exercise, and routines.
- Indian scientists like Dr. Kamal Ranadive (cancer research) and Dr. Maharaj Kishan Bhan (vaccine development) have made significant contributions.
Key Messages for Health Campaigns
- Health includes physical, mental, and social well-being.
- Prevent communicable diseases through hygiene, vaccination, and clean environments.
- Prevent non-communicable diseases with lifestyle choices: balanced diet, exercise, no tobacco/alcohol.
- Vaccines are for prevention, not for treating ongoing illness.
- Use antibiotics responsibly.
Sample Questions and Answers
1. Classify the following as communicable or non-communicable: Diabetes, Typhoid, Asthma, Measles.
- Answer: Communicable—Typhoid, Measles; Non-communicable—Diabetes, Asthma.
2. What immediate actions should be taken during a flu outbreak in school?
- Answer: Isolate sick students, encourage handwashing, sanitize surfaces, cover mouth/nose while sneezing/coughing, and ventilate classrooms.
3. Why are vaccines important?
- Answer: Vaccines train the immune system to recognize and fight specific diseases, preventing outbreaks and saving lives.
4. Why should antibiotics not be taken for viral infections like the flu?
- Answer: Antibiotics only kill bacteria, not viruses. Unnecessary use can lead to bacteria becoming resistant, causing bigger health problems.
5. Which diseases spread if drinking water is contaminated by feces?
- Answer: Hepatitis A, Poliomyelitis, and Cholera can spread through contaminated water, but not Tuberculosis or Chickenpox.
6. What preventive steps can reduce mosquito-borne diseases like dengue and malaria?
- Answer: Use mosquito nets, apply repellents, avoid water stagnation, keep surroundings clean, and wear long-sleeved clothing.
These notes and questions are structured to help students understand Chapter 3 comprehensively and prepare for tests and class activities.
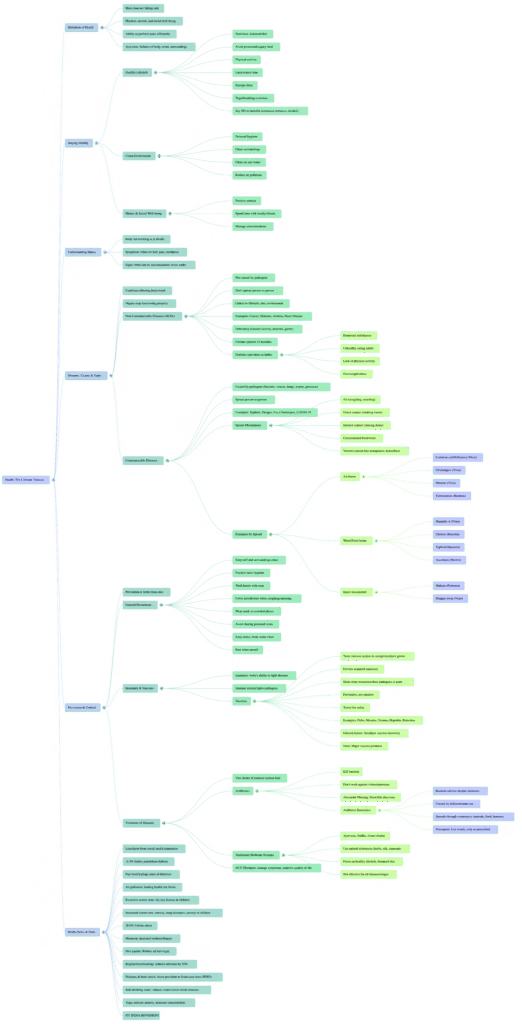
Mind-map of Chapter 3: The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye
20 MCQs with answer key
Here are 20 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) based on NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 3, “Health: The Ultimate Treasure,” along with the answer key:
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
- How does the WHO define health?
a) Absence of disease
b) Complete physical, mental, and social well-being
c) Ability to do physical work only
d) Being happy all the time - Which of the following is NOT an aspect of health?
a) Physical
b) Emotional
c) Social
d) Financial - Which habit is good for maintaining health?
a) Eating fast food regularly
b) Skipping breakfast
c) Regular exercise
d) Excessive screen time - Pathogens cause which type of diseases?
a) Non-communicable
b) Communicable
c) Chronic
d) Allergic - Which of the following spreads diseases by acting as a vector?
a) Cockroach
b) Mosquito
c) Housefly
d) Earthworm - What type of disease is diabetes?
a) Communicable
b) Non-communicable
c) Infectious
d) Deficiency disease - Which of these is a preventive measure for communicable diseases?
a) Taking antibiotics unnecessarily
b) Vaccination
c) Smoking
d) Skipping meals - What is the main cause of antibiotic resistance?
a) Using antibiotics only when prescribed
b) Not taking antibiotics at all
c) Misusing or overusing antibiotics
d) Eating healthy food - Which of the following diseases spreads through contaminated water?
a) Chickenpox
b) Typhoid
c) Influenza
d) Measles - Which disease is caused by virus?
a) Cholera
b) Tuberculosis
c) Common cold
d) Ascariasis - What is the main purpose of vaccination?
a) Cure disease after infection
b) Kill all bacteria in the body
c) Train immune system to fight specific diseases
d) Increase body weight - Which disease was eradicated using vaccination?
a) Polio
b) Smallpox
c) Measles
d) Dengue - The term “vector” is used to describe
a) Disease-causing bacteria
b) Organisms that carry pathogens from one host to another
c) Immune cells
d) Vaccines - Which of the following is NOT a good habit to stay healthy?
a) Balanced diet
b) Adequate sleep
c) Smoking cigarettes
d) Regular physical activity - The first antibiotic discovered was
a) Penicillin
b) Aspirin
c) Vaccines
d) Tetanus - The excessive use of antibiotics can lead to
a) Quick recovery from all diseases
b) Resistance in bacteria
c) Increased immunity
d) No side effects - Which among the following is classified as a deficiency disease?
a) Diabetes
b) Cancer
c) Scurvy
d) Flu - What is a symptom of a disease?
a) Rash that can be seen
b) Pain that a person feels
c) High temperature measured by thermometer
d) Swelling of body parts - How can communicable diseases spread?
a) Through air, direct contact, contaminated food and water
b) Only by water
c) Only by food
d) Only by animals - Which of the following helps maintain a healthy mind?
a) Spending a lot of time alone
b) Regularly talking and spending time with friends and family
c) Avoiding social interactions
d) Too much screen time
Answer Key
- b
- d
- c
- b
- b
- b
- b
- c
- b
- c
- c
- b
- b
- c
- a
- b
- c
- b
- a
- b
This MCQ quiz covers definitions, concepts, preventive measures, and facts from the chapter, suitable for classroom or exam preparation.
